Comparison of Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure: Pricing, Benefits, and Features
As businesses increasingly turn to cloud computing for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, three major players dominate the landscape: Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure. Each platform has its strengths, features, and pricing models, making it crucial for organizations to understand how they compare. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure, focusing on their pricing, benefits, and features.
1. Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows businesses to access and manage data and applications over the internet rather than relying on local servers or personal computers. The key models of cloud computing include:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, allowing developers to build applications without managing the infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
The three major cloud service providers—GCP, AWS, and Azure—offer services across these models, catering to different business needs.
2. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
a. Overview
Launched in 2006, AWS is the oldest and most widely adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. AWS provides a robust, flexible, and secure cloud computing environment that is popular among startups and large enterprises.
b. Pricing
AWS employs a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use. Pricing is structured around:
- On-Demand Pricing: Users pay for compute capacity by the hour with no long-term contracts.
- Reserved Instances: Users commit to using a specific instance type for a one- or three-year term, resulting in significant savings.
- Spot Instances: Users can bid for unused capacity at a lower rate, which is cost-effective for flexible workloads.
Example Pricing:
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Pricing starts at approximately $0.0116 per hour for a t2.micro instance.
- S3 (Simple Storage Service): Storage pricing starts at $0.023 per GB for the first 50 TB.
c. Benefits and Features
- Extensive Service Portfolio: AWS offers a vast range of services, including computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and analytics.
- Global Infrastructure: With a presence in 81 Availability Zones across 25 regions, AWS provides high availability and redundancy.
- Scalability: AWS allows users to scale resources up or down as needed, accommodating fluctuating workloads.
- Security and Compliance: AWS provides a robust security framework, including data encryption and compliance with major regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
3. Microsoft Azure
a. Overview
Microsoft Azure, launched in 2010, is a comprehensive cloud platform that integrates with Microsoft products and services. It offers a wide range of cloud services, including computing, analytics, storage, and networking.
b. Pricing
Azure also uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model with various pricing options:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Users are charged based on their consumption of resources.
- Reserved Instances: Customers can save up to 72% by committing to a one- or three-year plan.
- Spot VMs: Users can bid for unused compute capacity at reduced prices.
Example Pricing:
- Virtual Machines: Pricing starts at approximately $0.008 per hour for a B1S instance.
- Blob Storage: Starts at $0.0184 per GB for the first 50 TB.
c. Benefits and Features
- Integration with Microsoft Products: Azure seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft services, such as Office 365 and Dynamics 365, providing a familiar environment for users.
- Hybrid Capabilities: Azure supports hybrid cloud solutions, allowing businesses to connect on-premises infrastructure with the cloud.
- Robust AI and Machine Learning Tools: Azure provides advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI services, making it a preferred choice for data-driven businesses.
- Security and Compliance: Azure emphasizes security, offering features like Azure Security Center and compliance with major standards.
4. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
a. Overview
Google Cloud Platform, launched in 2008, focuses on providing a wide range of services including computing, data storage, data analytics, and machine learning. GCP is known for its strengths in data analytics and machine learning.
b. Pricing
GCP employs a straightforward pricing model that includes:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Users are charged based on their actual usage of resources.
- Sustained Use Discounts: Automatically applies discounts when services are used for extended periods.
- Committed Use Contracts: Customers can commit to using GCP services for one or three years in exchange for lower prices.
Example Pricing:
- Compute Engine: Pricing starts at approximately $0.0100 per hour for an f1-micro instance.
- Cloud Storage: Pricing starts at $0.020 per GB for the first 1 TB.
c. Benefits and Features
- Data Analytics and Big Data Solutions: GCP excels in data analytics and machine learning with tools like BigQuery and TensorFlow.
- Open Source and Hybrid Cloud Flexibility: GCP supports Kubernetes and other open-source technologies, making it easier to deploy applications across different environments.
- Network Infrastructure: GCP benefits from Google’s global network infrastructure, providing high-speed connections and low latency.
- Security: GCP employs a robust security model with features such as data encryption, identity management, and compliance with various regulations.
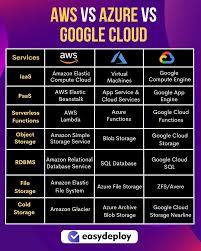
5. Feature Comparison
Here’s a comparative overview of the key features of AWS, Azure, and GCP:
| Feature | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service Portfolio | Extensive (200+ services) | Extensive (200+ services) | Focus on Data/ML (100+ services) |
| Global Infrastructure | 81 Availability Zones | 60+ Regions | 29 Regions |
| Pricing Models | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved, Spot | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved, Spot | Pay-as-you-go, Sustained Discounts, Committed Use |
| Compute Services | EC2, Lambda | Virtual Machines, Functions | Compute Engine, Cloud Functions |
| Storage Services | S3, EBS, Glacier | Blob Storage, File Storage | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disks |
| AI & ML Services | SageMaker, Deep Learning | Azure ML, Cognitive Services | AI Platform, BigQuery ML |
| Hybrid Cloud Support | Limited | Strong | Strong |
| Security Compliance | Comprehensive | Comprehensive | Comprehensive |
6. Choosing the Right Cloud Provider
When selecting a cloud provider, businesses should consider the following factors:
a. Business Requirements
Identify your business’s specific needs—whether it’s computational power, storage capacity, machine learning capabilities, or hybrid cloud solutions. This will help narrow down the options.
b. Existing Technology Stack
Consider how well the cloud provider integrates with your existing technology stack. For instance, businesses heavily reliant on Microsoft products may benefit from Azure’s seamless integration.
c. Cost Considerations
Analyze the pricing models of each provider based on your anticipated usage. It’s essential to consider both short-term and long-term costs, including potential savings from reserved instances or committed use contracts.
d. Scalability and Flexibility
Evaluate each provider’s ability to scale resources up or down as needed. This flexibility can significantly affect your operational efficiency and cost management.
e. Support and Documentation
Examine the support options available from each provider, including customer service, documentation, and community resources. A strong support network can greatly enhance the user experience.
7. Conclusion
In the competitive landscape of cloud computing, Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure each offer unique benefits, features, and pricing models tailored to meet diverse business needs. AWS stands out for its extensive service portfolio and global infrastructure, while Azure excels in integration with Microsoft products and hybrid cloud capabilities. GCP is a strong contender in data analytics and machine learning, making it ideal for businesses focused on big data.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your specific business requirements, existing technology stack, and budget considerations. By carefully assessing these factors, businesses can select the cloud provider that best aligns with their objectives, ensuring a successful cloud journey.