AI for Managing Mixed Traffic Environments with Autonomous Vehicles
The advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs) is revolutionizing the transportation landscape, promising safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly mobility. However, the transition to fully autonomous transportation systems will not occur overnight. For the foreseeable future, autonomous vehicles will share the roads with human-driven cars, bicycles, pedestrians, and other road users in complex, mixed-traffic environments. Managing these interactions is a daunting challenge, but Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers innovative solutions to ensure safety, efficiency, and harmony in such scenarios.
This article explores the role of AI in managing mixed-traffic environments, the technologies involved, challenges, and the path forward to seamless integration.
The Complexity of Mixed-Traffic Environments
Mixed-traffic environments encompass a variety of road users:
- Human-Driven Vehicles: Vehicles operated by humans, with unpredictable behaviors and varying driving skills.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Equipped with sensors and AI systems, designed to follow programmed rules and adapt to their surroundings.
- Non-Motorized Road Users: Cyclists and pedestrians, who often move unpredictably.
- Public Transport Systems: Buses and trams with fixed routes and schedules.
These diverse entities interact in dynamic and often chaotic ways, creating challenges such as:
- Behavioral Uncertainty: Human drivers, pedestrians, and cyclists often act in ways that are difficult for machines to predict.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Roads, signals, and signs are designed for human interpretation, which may not align with autonomous systems.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Decisions in complex scenarios, such as avoiding collisions, may involve ethical trade-offs.
AI-powered systems are essential to address these challenges and enable autonomous vehicles to coexist safely and efficiently in mixed-traffic settings.
AI’s Role in Managing Mixed-Traffic Environments
AI technologies empower autonomous vehicles and traffic management systems to handle the complexities of mixed-traffic environments. Key AI-driven functionalities include:
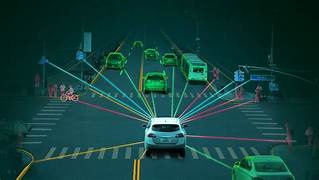
1. Perception and Awareness
Autonomous vehicles rely on AI-powered perception systems to understand their surroundings. These systems use data from cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to:
- Identify and track nearby vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists.
- Recognize traffic signals, road signs, and lane markings.
- Detect hazards such as road debris or sudden obstacles.
Machine learning algorithms enhance the accuracy of these perception systems by learning from vast datasets of road scenarios, enabling AVs to respond appropriately in real time.
2. Behavior Prediction
One of the most significant challenges in mixed-traffic environments is predicting the behavior of human drivers and other road users. AI-driven models analyze historical and real-time data to forecast:
- Whether a pedestrian will cross the road.
- If a cyclist will change lanes or turn.
- How a human driver may react to a merging vehicle.
These predictions allow AVs to anticipate potential conflicts and adjust their actions accordingly.
3. Decision-Making and Planning
AI systems enable AVs to make decisions in complex scenarios by:
- Prioritizing safety while minimizing disruptions to traffic flow.
- Balancing the need for assertiveness with caution to navigate effectively around human-driven vehicles.
- Adapting routes dynamically to avoid congestion or accidents.
Reinforcement learning, a subset of AI, helps AVs optimize decision-making by learning from simulated or real-world experiences.
4. Communication and Collaboration
In mixed-traffic environments, effective communication between road users is crucial. AI facilitates:
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication: AVs share information about their location, speed, and intentions with other vehicles.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: AVs interact with traffic signals, infrastructure, and even pedestrians using connected technologies.
This communication fosters better coordination, reducing the likelihood of accidents and improving traffic flow.
5. Traffic Flow Optimization
AI-driven traffic management systems analyze real-time data to optimize traffic flow by:
- Adjusting signal timings based on traffic density.
- Recommending speed adjustments to reduce congestion.
- Identifying and mitigating accident-prone areas.
These systems benefit both autonomous and human-driven vehicles, creating a more efficient transportation network.
Applications of AI in Mixed-Traffic Management
AI technologies are being deployed in various ways to manage mixed-traffic environments effectively:
1. Smart Traffic Systems
AI-powered traffic systems use sensors and cameras to monitor road conditions and manage traffic signals dynamically. For example:
- In Singapore, smart traffic lights adjust timings based on pedestrian and vehicle flow.
- AI algorithms in Los Angeles help reduce congestion by synchronizing signals.
2. Pedestrian Safety Systems
AI improves pedestrian safety by enabling AVs to:
- Recognize pedestrian gestures, such as raised hands indicating an intention to cross.
- Predict pedestrian movements even in crowded or low-visibility conditions.
- Alert human drivers about pedestrians in their blind spots.
3. Urban Mobility Platforms
Ride-sharing and public transport platforms integrate AI to:
- Plan routes that minimize conflicts between AVs and other road users.
- Coordinate pick-ups and drop-offs in busy areas without disrupting traffic.
4. Autonomous Vehicle Training
AI-powered simulators expose AVs to diverse scenarios, including interactions with human drivers and pedestrians. These virtual environments allow AVs to learn and improve without real-world risks.
Benefits of AI in Mixed-Traffic Environments
The integration of AI in managing mixed-traffic environments offers numerous advantages:
1. Enhanced Safety
AI reduces accidents by predicting and mitigating risks, ensuring AVs respond appropriately to unpredictable human behavior.
2. Increased Efficiency
Optimized traffic flow reduces congestion, travel times, and fuel consumption, benefiting all road users.
3. Better User Experience
Smooth interactions between AVs and other road users enhance the overall transportation experience, encouraging public trust in autonomous technology.
4. Environmental Impact
Efficient traffic management lowers emissions, contributing to cleaner and more sustainable urban environments.
Challenges in AI-Driven Mixed-Traffic Management
Despite its potential, AI faces several challenges in managing mixed-traffic environments:
1. Data Limitations
AI models require vast amounts of high-quality data to function effectively. Data gaps or biases can compromise their accuracy.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
Governments must establish clear regulations to guide the deployment of AI in transportation, balancing innovation with public safety.
3. Ethical Dilemmas
AI systems must navigate ethical questions, such as prioritizing the safety of different road users in unavoidable collision scenarios.
4. Infrastructure Readiness
Adapting existing infrastructure to support AI-driven systems, such as installing sensors and communication networks, requires significant investment.
5. Public Acceptance
Gaining public trust in AI-driven systems is essential, particularly in scenarios involving interactions between AVs and human drivers.
The Future of AI in Mixed-Traffic Management
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in managing mixed-traffic environments will expand, driven by advancements in areas such as:
1. Multi-Agent Collaboration
Future AI systems will coordinate multiple autonomous and human-driven vehicles, creating a cohesive and harmonious traffic ecosystem.
2. Context-Aware AI
AI models will incorporate contextual factors, such as weather conditions and cultural norms, to make more nuanced decisions.
3. Global Standards
The establishment of international standards for V2X communication and AI safety protocols will enable seamless integration across borders.
4. Continuous Learning
AI systems will adopt lifelong learning approaches, adapting to new traffic scenarios and evolving behaviors.
5. Integration with Smart Cities
AI will become a cornerstone of smart city initiatives, enabling holistic solutions that encompass transportation, energy, and infrastructure.
Conclusion
AI is a game-changer in managing mixed-traffic environments, offering innovative solutions to ensure the seamless coexistence of autonomous vehicles, human-driven cars, and other road users. By leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and V2X communication, AI can enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience in complex traffic scenarios.
While challenges such as data limitations, ethical dilemmas, and infrastructure readiness persist, ongoing advancements in AI and collaboration between stakeholders promise a future where mixed-traffic environments operate harmoniously. As we move towards this vision, AI will play a pivotal role in shaping the transportation systems of tomorrow, paving the way for safer, smarter, and more sustainable mobility.