The Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Computing Technology: An In-Depth Exploration
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals manage, store, and process data. By offering on-demand access to computing resources such as servers, storage, and software, cloud computing provides unprecedented flexibility and scalability. However, as with any transformative technology, it comes with its own set of benefits and challenges. In this article, we’ll delve into the key advantages and drawbacks of cloud computing to provide a comprehensive understanding of its impact on modern technology.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more—over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, users can access these resources via the cloud, often on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Cloud computing is typically categorized into three main service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a platform and tools for developers to build, test, and deploy applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation.
Now, let’s explore the benefits and challenges associated with this technology.
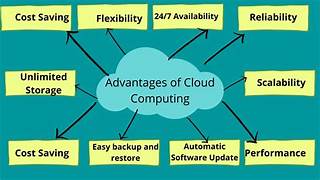
Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is cost savings. Traditional IT infrastructure requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and maintenance. With cloud computing, businesses can eliminate these expenses by using resources on an as-needed basis.
- No Upfront Costs: Companies don’t need to purchase expensive servers or equipment.
- Pay-as-You-Go: Businesses only pay for the resources they use, reducing wasteful spending.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Cloud service providers handle updates, maintenance, and security, reducing the need for in-house IT staff.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing allows organizations to scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- Scalable Resources: Companies can quickly add more storage or processing power during peak times.
- Global Reach: Cloud services enable businesses to expand into new regions without significant infrastructure investment.
- Flexibility for Remote Work: Employees can access data and applications from anywhere, facilitating remote and hybrid work models.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud computing promotes collaboration by allowing teams to access, edit, and share documents and applications in real-time. This fosters efficiency and improves communication across teams, especially for remote or distributed workforces.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Multiple users can work on the same document or project simultaneously.
- Access from Anywhere: Employees can work from any location, using any device with internet connectivity.
- Centralized Data: Cloud platforms ensure that everyone is working with the most up-to-date information.
4. Improved Disaster Recovery and Backup
Data loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters can be catastrophic for businesses. Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery and backup solutions.
- Automatic Backups: Many cloud services provide automatic data backups, reducing the risk of data loss.
- Redundancy: Cloud providers often store data across multiple locations to ensure its safety and accessibility.
- Faster Recovery: Businesses can quickly restore operations after a disruption by accessing their data from the cloud.
5. Innovation and Agility
Cloud computing empowers businesses to innovate by providing access to advanced tools and technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics.
- Faster Development Cycles: Cloud platforms enable rapid testing and deployment of new applications.
- Access to Advanced Tools: Businesses can use AI, ML, and analytics without investing in expensive infrastructure.
- Adaptability: Cloud services allow businesses to respond quickly to market changes and emerging trends.
Challenges of Cloud Computing
1. Security and Privacy Concerns
While cloud providers invest heavily in security, the centralized nature of cloud storage makes it a potential target for cyberattacks.
- Data Breaches: Storing sensitive information in the cloud increases the risk of unauthorized access.
- Compliance Issues: Businesses in regulated industries may face challenges in meeting data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Shared Responsibility: Cloud security often requires both the provider and the customer to implement security measures, leading to potential gaps.
2. Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Cloud computing relies on stable and high-speed internet connectivity. Any disruption in connectivity can lead to service interruptions.
- Downtime: Without internet access, users cannot access cloud-based applications or data.
- Latency Issues: Applications that require real-time processing may experience delays if the network is slow.
- Limited Accessibility in Remote Areas: Regions with poor internet infrastructure may struggle to fully leverage cloud computing.
3. Vendor Lock-In
Businesses that adopt cloud computing may become dependent on a specific provider’s services, making it difficult to switch vendors or migrate data.
- Compatibility Issues: Moving applications or data to a new provider can be complex and time-consuming.
- Proprietary Tools: Some cloud providers use proprietary tools and formats, complicating integration with other platforms.
- Cost Implications: Switching providers may involve significant costs and potential downtime.
4. Cost Management Challenges
While cloud computing is cost-effective, improper management can lead to unexpected expenses.
- Over-Provisioning: Businesses may pay for resources they don’t fully utilize.
- Hidden Costs: Additional charges for data transfer, storage, or premium services can add up.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Effective cost management requires continuous monitoring of usage and optimization of resources.
5. Limited Control and Customization
By outsourcing infrastructure and services to cloud providers, businesses may lose some level of control over their IT environment.
- Standardized Solutions: Cloud providers often offer standardized services that may not fully align with a company’s unique requirements.
- Dependency on Providers: Businesses rely on providers to implement updates, fix issues, and maintain services.
- Lack of Customization: Some cloud platforms may not support highly customized configurations.
6. Data Transfer and Latency Issues
Moving large volumes of data to and from the cloud can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Bandwidth Costs: Transferring data between local systems and the cloud may incur significant bandwidth charges.
- Latency: Applications that require real-time data processing may experience delays due to network latency.
- Data Sovereignty: Organizations must ensure compliance with local data sovereignty laws, which can complicate cloud adoption.
Striking the Right Balance
To fully leverage the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing its challenges, businesses should adopt a strategic approach:
- Evaluate Business Needs: Assess your organization’s specific requirements to determine whether cloud computing is the right fit.
- Choose the Right Provider: Compare cloud providers based on factors like pricing, security, scalability, and customer support.
- Implement Security Best Practices: Use encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular audits to enhance cloud security.
- Monitor Costs: Continuously track usage and optimize resource allocation to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Adopt a Hybrid Approach: Consider a hybrid cloud model that combines on-premises and cloud resources to balance control and flexibility.
Conclusion
Cloud computing technology offers transformative benefits, from cost savings and scalability to enhanced collaboration and disaster recovery. However, it also presents challenges such as security concerns, vendor lock-in, and cost management issues. By understanding these benefits and challenges, businesses can make informed decisions about adopting cloud computing and maximizing its potential. As technology continues to evolve, the cloud will remain a critical component of modern IT infrastructure, driving innovation and shaping the future of how we work and interact with technology.