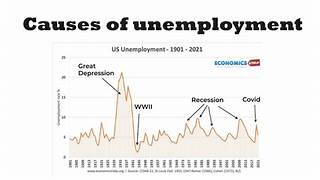
“Factors Affecting the Duration of Unemployment and Job Searches”.
Introduction
- Definition of Unemployment and Job Search:
- Unemployment is the state of being jobless while actively seeking work. Job search refers to the process of seeking and applying for new job opportunities.
- The duration of unemployment and the job search process can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors is key to addressing the challenges faced by unemployed individuals.
- Importance of the Topic:
- The length of unemployment can have serious consequences for individuals, economies, and societies. Long-term unemployment can result in skills deterioration, economic instability, and social disillusionment. Identifying the factors that affect the duration of unemployment can inform policies and interventions to reduce job search time and improve employment outcomes.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Unemployment
- Economic Conditions:
- Recession vs. Economic Growth: The state of the economy plays a crucial role in determining how long individuals remain unemployed. During economic recessions, businesses are less likely to hire, leading to longer periods of unemployment. Conversely, during economic growth, job opportunities are more abundant, potentially reducing unemployment duration.
- Industry-Specific Decline or Growth: Certain sectors may experience growth while others face downturns. For instance, technology and healthcare industries might grow even during economic slowdowns, while industries like retail and manufacturing might struggle.
- Labor Market Conditions: A mismatch between the number of job seekers and available job openings can lengthen the unemployment duration. If the supply of workers exceeds demand in certain fields, it may take longer to find suitable employment.
- Individual Characteristics:
- Education and Skill Level: Higher levels of education and specialized skills often correlate with shorter job search durations. Highly skilled workers tend to find positions quicker due to the specific nature of their expertise. In contrast, those with lower education levels or general skills may struggle more to find suitable positions.
- Experience: Job seekers with more work experience may have an advantage in securing new employment, as employers often value experienced candidates. However, those who are newly entering the job market or have a gap in their work history may face longer unemployment periods.
- Age and Demographics: Younger workers may face shorter unemployment durations as they are often more flexible and willing to accept entry-level roles. Older workers, particularly those nearing retirement age, may face age-related discrimination or have difficulty adapting to rapidly changing job markets, which can lengthen their unemployment duration.
- Gender and Diversity: Gender and diversity factors can influence job search duration. Women and minorities, especially those from marginalized communities, may experience longer unemployment periods due to bias or discrimination in hiring processes.
- Job Search Strategies and Efforts:
- Proactive vs. Passive Job Search: Job seekers who actively network, apply to multiple jobs, and engage with hiring platforms tend to find employment faster. On the other hand, passive job seekers who only apply to a limited number of positions or rely on traditional methods may experience longer periods of unemployment.
- Job Search Skills: Effective job search skills, such as tailoring resumes and cover letters, preparing for interviews, and leveraging online job boards, can reduce job search duration. Those who are not familiar with these strategies or lack confidence may take longer to secure employment.
- Use of Social Networks: Networking plays a critical role in reducing the length of job searches. People who can connect with potential employers, mentors, or industry professionals are often able to find job opportunities more quickly. A well-established social network can be invaluable for job seekers.
- Government Policies and Social Support Systems:
- Unemployment Benefits: Access to unemployment benefits can provide a financial cushion for individuals while they search for work. In some cases, these benefits also encourage individuals to stay unemployed longer, as they may not feel an immediate pressure to accept the first available job. Conversely, lack of financial support may push people to accept jobs quickly, regardless of whether they are a good match.
- Job Training and Employment Programs: Government-run programs designed to improve job-seeking skills or provide additional training can help reduce unemployment durations by making workers more marketable. These programs help individuals acquire in-demand skills and increase their chances of finding a job.
- Labor Market Regulations: In some countries, regulations around hiring and firing, such as minimum wage laws, job security protections, or labor union activity, can impact the speed at which employers are willing to hire and the stability of employment. More flexible labor markets may allow for quicker employment, while rigid systems could result in longer search times.
- Personal and Psychological Factors:
- Motivation and Mental Health: Job seekers with high motivation and a positive attitude tend to persist in their search for longer periods, leading to faster employment. However, individuals who experience feelings of hopelessness or depression may struggle to maintain consistent efforts in their job search, which can prolong unemployment.
- Job Search Fatigue: Prolonged unemployment can lead to fatigue, frustration, and burnout, which may reduce the effectiveness of the job search. Mental and emotional exhaustion can negatively affect the energy and persistence needed to continue applying for jobs.
- Support Systems and Social Networks: Strong support systems, including family, friends, and mentors, can reduce the emotional strain of unemployment and provide guidance and encouragement. A lack of support, on the other hand, can increase stress and negatively affect the job search duration.
- Geographic Location and Mobility:
- Regional Job Market Conditions: The job market can vary significantly from one region to another. Urban areas typically offer more opportunities, but they may also have more competition. In rural areas, job opportunities may be scarce, leading to longer unemployment durations.
- Willingness to Relocate: Those willing to relocate for a job may reduce their unemployment duration significantly. Geographic flexibility allows job seekers to cast a wider net, increasing their chances of finding employment. On the other hand, those unwilling or unable to move may face longer job searches due to limited local opportunities.
Consequences of Extended Unemployment Duration
- Economic Impact: Prolonged unemployment contributes to the loss of productivity and potential output in an economy. It also leads to increased government spending on unemployment benefits and social services, which places a burden on public finances.
- Skills Deterioration: As unemployment stretches over time, workers may experience skills deterioration, particularly if their previous job roles are rapidly evolving or if the labor market demands newer skills. This creates a vicious cycle where the longer someone is unemployed, the harder it becomes for them to re-enter the workforce.
- Social and Psychological Impact: The longer the unemployment period, the greater the negative effects on individuals’ mental health and social well-being. Prolonged unemployment can lead to depression, anxiety, and increased social exclusion, making it more difficult for individuals to reintegrate into the workforce.
Strategies to Reduce Unemployment Duration
- Targeted Job Creation: Governments and private sectors can invest in industries or regions with high unemployment rates, encouraging job creation and reducing labor market imbalances.
- Skills Training and Education: Providing opportunities for workers to upskill or reskill in areas with high demand can reduce unemployment duration, particularly for individuals whose skills have become obsolete due to technological advancements.
- Improved Job Search Assistance: Expanding access to job search resources, career counseling, and resume building workshops can significantly reduce job search time. Support systems, such as job fairs, mentorship programs, and online platforms, can connect job seekers with potential employers faster.
- Encouraging Mobility and Relocation: Policies that encourage geographic mobility, such as relocation grants or housing assistance, can help individuals access job opportunities in regions with more favorable employment conditions.
- Mental Health and Motivation Support: Providing emotional support and addressing mental health issues can help job seekers maintain motivation and stay proactive in their search for work.
Conclusion
- Summary of Factors: The duration of unemployment and job searches is influenced by economic conditions, individual characteristics, job search strategies, government policies, and personal factors. Understanding these variables can help in developing strategies to reduce job search durations and improve employment outcomes.
- Call to Action: Reducing the duration of unemployment requires a multi-faceted approach, including policies aimed at creating jobs, improving skills, supporting mental health, and facilitating job search efforts. By addressing these factors, societies can not only reduce unemployment but also create more robust and resilient labor markets.
- Final Thought: The challenges associated with unemployment are complex, but by tackling the various factors that contribute to prolonged job searches, we can work toward a more inclusive and dynamic economy.