A Research Study on Employee Salary Plans and Strategies for Paying Taxes
Introduction
Employee compensation is a critical aspect of workforce management, impacting job satisfaction, productivity, and financial stability. Alongside salary structures, employees must strategize their tax payments effectively to maximize income retention. This research study examines different salary plans, tax obligations, and strategies employees can adopt to manage their taxes efficiently.
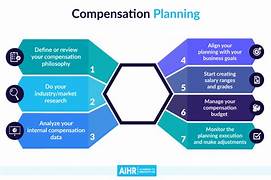
1. Understanding Employee Salary Plans
Salary plans vary across industries and job roles, influencing how employees earn and manage their finances. The primary salary structures include:
a. Fixed Salary Plan
- Employees receive a predetermined amount per month.
- Common in corporate, government, and contractual roles.
- Offers stability but may lack incentives for exceptional performance.
b. Hourly Wage Plan
- Employees are paid based on hours worked.
- Common in retail, manufacturing, and service industries.
- Provides flexibility but may lead to inconsistent income.
c. Performance-Based Compensation
- Includes commissions, bonuses, and profit-sharing.
- Encourages productivity and goal achievement.
- Variability in earnings can make financial planning challenging.
d. Equity-Based Compensation
- Employees receive stock options or shares.
- Popular in startups and tech firms.
- Potential for high earnings but subject to market volatility.
2. Employee Tax Obligations
Understanding tax obligations is essential for financial planning. Taxes deducted from salaries include:
a. Income Tax
- Federal and state governments tax employee earnings based on income brackets.
- Progressive tax rates apply in most countries.
b. Payroll Taxes
- Includes Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment contributions.
- Employers and employees share the tax burden.
c. Benefits and Taxation
- Health insurance, retirement plans, and allowances may have tax implications.
- Some benefits are tax-exempt, reducing overall taxable income.
3. Strategies for Employees to Manage Taxes
Employees can optimize their tax payments through various strategies:
a. Tax Withholding Adjustments
- Employees can adjust W-4 forms (U.S.) or tax declarations to ensure proper withholding.
- Over-withholding leads to refunds, while under-withholding may cause tax liabilities.
b. Utilizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts
- Contributions to retirement accounts (401(k), IRA) reduce taxable income.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSA) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA) offer tax benefits.
c. Claiming Deductions and Credits
- Work-related expenses, student loan interest, and childcare costs may be deductible.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) benefits lower-income workers.
d. Planning for Bonuses and Equity Compensation
- Employees can defer bonuses or sell stock options strategically to minimize tax impact.
- Consulting a tax professional ensures optimal tax treatment.
4. Employer Role in Salary and Tax Planning
Employers assist in tax planning by:
- Offering tax-advantaged benefits like employer-matched retirement contributions.
- Providing educational resources and tax workshops.
- Ensuring accurate payroll tax calculations and compliance.
Conclusion
Effective salary planning and tax strategies benefit both employees and employers. Understanding different compensation structures, tax obligations, and proactive tax management techniques enables employees to optimize their earnings and financial security. Employers also play a role in facilitating tax-efficient salary plans, ensuring compliance, and supporting employees’ financial well-being.