Comparing the Classic and Modern Methods of Project Management
Introduction
Project management is a critical discipline that ensures the successful execution of projects within an organization. Over the years, project management methodologies have evolved significantly, transitioning from traditional approaches to modern, flexible methods that cater to the complexities of today’s fast-paced business environment. This article explores the differences between classic and modern project management techniques, highlighting their advantages, limitations, and applications.
Understanding Classic Project Management Methods
Classic project management refers to traditional methodologies that follow a structured and sequential process. These methods are characterized by well-defined phases, strict documentation, and rigid planning.
1. Waterfall Method
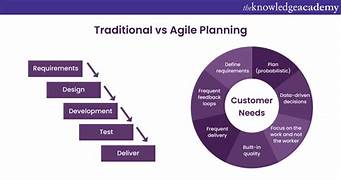
The Waterfall model is one of the most well-known traditional project management methodologies. It follows a linear sequence, where each phase must be completed before the next one begins. The key phases include:
- Requirement Gathering
- Design
- Implementation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Advantages:
- Clear structure and documentation
- Well-defined roles and responsibilities
- Easy to track progress
- Suitable for projects with stable and clear requirements
Limitations:
- Inflexibility to changes
- High risk of failure if issues arise late in the project
- Lengthy development cycles
- Difficulties in adapting to evolving customer needs
2. Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is a technique used for scheduling project activities, ensuring tasks are completed in the shortest time possible. It focuses on identifying the most critical tasks that directly impact the project timeline.
Advantages:
- Effective resource allocation
- Helps in time management
- Improves project predictability
Limitations:
- Does not accommodate uncertainties well
- Complex for large-scale projects with numerous dependencies
Understanding Modern Project Management Methods
Modern project management methodologies emphasize flexibility, collaboration, and adaptability. They are designed to accommodate changing project requirements and technological advancements.
1. Agile Methodology
Agile project management focuses on iterative development, continuous feedback, and customer collaboration. Instead of a linear approach, Agile divides the project into small increments called sprints, which are delivered in cycles.
Advantages:
- Highly adaptable to changes
- Encourages teamwork and communication
- Continuous customer feedback improves product quality
- Faster delivery of project components
Limitations:
- Requires a highly skilled and collaborative team
- Can be challenging to implement in rigid corporate environments
- Lack of comprehensive documentation
2. Scrum Framework
Scrum is an Agile framework that focuses on managing complex projects with short, iterative development cycles. Teams work in time-boxed sprints, with regular meetings (daily stand-ups) to track progress.
Advantages:
- Quick adaptability to changes
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Frequent deliverables enhance client satisfaction
Limitations:
- Requires continuous collaboration
- Can be difficult to manage in large-scale projects
3. Kanban Method
Kanban is a visual project management tool that helps teams track tasks in real-time. It uses a board with columns representing different stages of a project, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Completed.”
Advantages:
- Increases workflow transparency
- Enhances team collaboration
- Reduces bottlenecks in project execution
Limitations:
- Less structured compared to other methodologies
- Can be challenging for teams unfamiliar with visualization tools
Comparing Classic and Modern Methods
| Aspect | Classic Methods | Modern Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Rigid and structured | Highly flexible and adaptive |
| Approach | Sequential (Waterfall) | Iterative and incremental (Agile, Scrum) |
| Customer Involvement | Limited until project completion | Continuous feedback loop |
| Risk Management | Issues identified late | Early issue detection and resolution |
| Documentation | Extensive | Minimal, focuses on working solutions |
| Suitability | Large, predictable projects | Dynamic, fast-changing projects |
Choosing the Right Methodology
Organizations must consider several factors when selecting a project management methodology:
- Project Complexity: Large, well-defined projects may benefit from traditional methods, while evolving projects require Agile approaches.
- Stakeholder Expectations: If customers need frequent updates, modern methods like Scrum and Agile are preferable.
- Team Structure: Classic methods work well for hierarchical teams, whereas modern methods suit cross-functional teams.
- Resource Availability: Traditional methods require detailed planning, whereas Agile methods require continuous collaboration.
Conclusion
Both classic and modern project management methodologies have their unique strengths and challenges. While traditional methods like Waterfall and CPM provide structure and predictability, modern approaches like Agile, Scrum, and Kanban offer adaptability and rapid iteration. The choice between these methods depends on project requirements, organizational culture, and the need for flexibility. Ultimately, the best approach is often a hybrid model that integrates the strengths of both classic and modern methodologies to achieve optimal project outcomes.